Computer Network
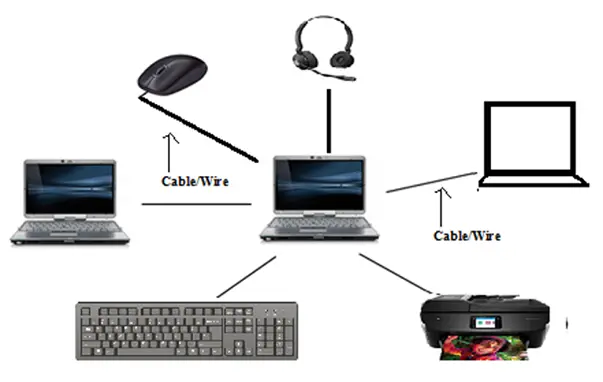
A computer network is a system that allows devices to share files, connect to the internet, communicate with one another, and improve communication efficiency. It enables the sharing of resources and data by connecting numerous PCs and electronic devices, including printers, tablets, and smartphones.
In simple terms, a computer network consists of two main components: nodes and links. Links are the connections that allow devices (nodes) to communicate with each other. Once devices are connected, they rely on communication rules, known as protocols, to send and receive information. The specific points where communication begins and ends are often referred to as ports.
Networks enable devices to communicate with each other through wired or wireless connections. These interactions are governed by specific protocols that define how data is transmitted and received.
Types of Computer Network
In general, networks can be classified from various perspectives, such as:
-
Geographical Distance
- A local area network serves a constrained space, like a house, workplace, or school.
- Wide Area Networks cover vast geographic areas, such as cities, nations, or the entire world.
- A city or a sizable campus is served by Metropolitan Area Network.
- Short-range networks for personal devices are called personal area networks.
-
Functional Role of Devices
- Peer-to-Peer all devices (peers) share responsibilities equally without a central server.
- Client-Server clients request services or resources from centralized servers.
-
Transmission Medium
- Radio waves or other wireless techniques are used by wireless network devices to communicate.
- Physical cables, such as Ethernet, are used to connect devices in wired networks.
Once a given network is configured,it should be good in performance,reliablility,and security.
Network devices
Hardware on a computer network can connect and communicate with one another via physical devices called network devices.
Hubs, repeaters, bridges, switches, routers, gateways, and routers are examples of network equipment that aid in controlling and guiding data flow inside a network.
By regulating data transfer, enhancing signals, and connecting various networks, they guarantee effective communication between linked devices. Every device has a distinct function, ranging from basic data forwarding to intricate network routing.
We can use any network device:
- To facilitate data transmission and reception between many devices.
- To Permit devices to safely and effectively connect to the network.
- To increases network speed and better controls data flow.
- To increase the network's coverage area and address signal issues.